Lamp Glossary of Terms
Acetylene Lamp – A lamp composed of a Regulator and Flasher that uses acetylene as a fuel.
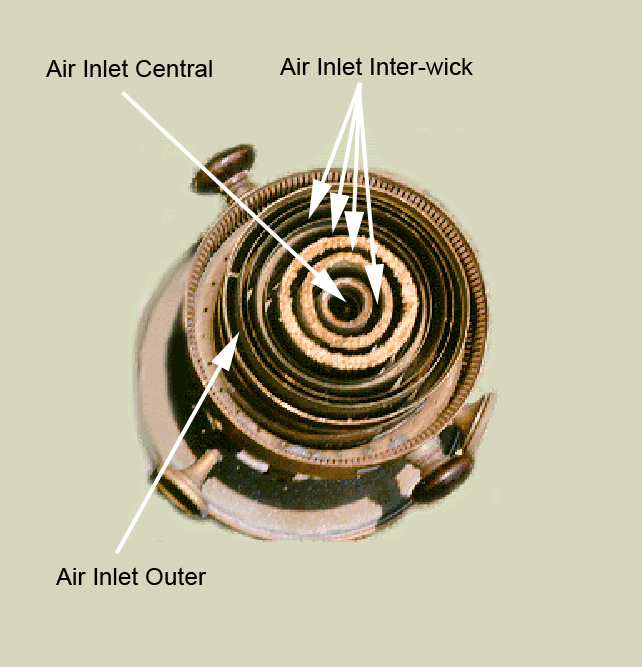
Air Inlet Central – The central metal tube inside the central wick in an Argand style lamp.
Air Inlet Inter-Wick – The opening(s) between the wicks in a multi-wick lamp.
Air Inlet Outer – The space around the exterior of the wick that is closest to the glass chimney.
Air Pressure Gauge – The means of determining the air pressure in an Air Pressure or an Incandescent Oil Vapor Lamp.
Air Pump – The pump (usually a bicycle style pump) used to maintain the pressure in an Air Pressure or an Incandescent Oil Vapor Lamp.
Argand – Ami Argand the inventor of the hollow wick capillary lamp.
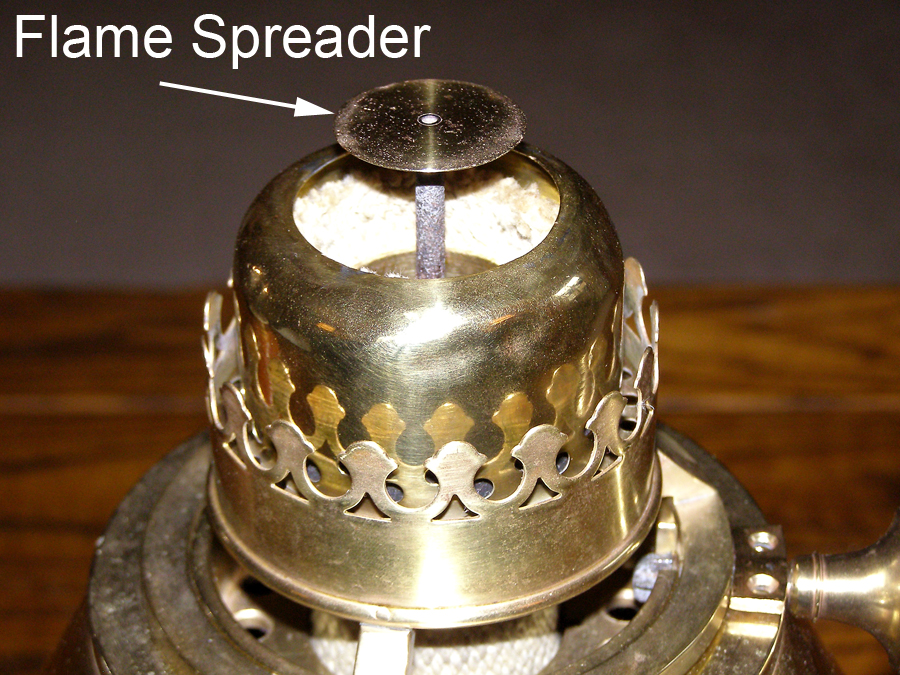
Burner – The part of the lamp where the flame is. This usually includes the area with the upper ends of the wicks and the flame spreader.
Button – See Flame Spreader.
Capillary – The physical action where the fuel is attracted up the surface of the wick, against gravity, due to the tiny spaces between the fibers of the wick.
Carcel – French Lamp maker and inventor of a clockwork mechanical pump that was used to pump fuel into the wick tubes to force the fuel to overflow the top of the wicks, thus cooling the burner.
Chimney – The glass tube placed around the flame that is used to force the air surrounding the outer wick to impinge upon the flame creating a brighter light.
Cistern – See Lower Reservoir.
Clockwork Pump – This pump was invented by Carcel and has one pump for each wick in a multi-wick burner. The pumps forced the fuel to overflow the top of each wick, thus cooling the burner.
Constant Level – A type of lamp using gravity feed where the level of the oil remains at a constant level on the wick. These lamps do not overflow the wick with fuel.
Drip Cup – A small cup or basin below the burner where any overflow fuel is collected.
Duplex Burner – A flat wick burner with two wicks.
Flame Spreader – A small rod topped with a flat or curved disc that is placed in the center of the flame, usually inside and above the ‘Air Inlet Central.’ This Flame Spreader does just that – it spreads the flame toward the chimney making it produce more light.
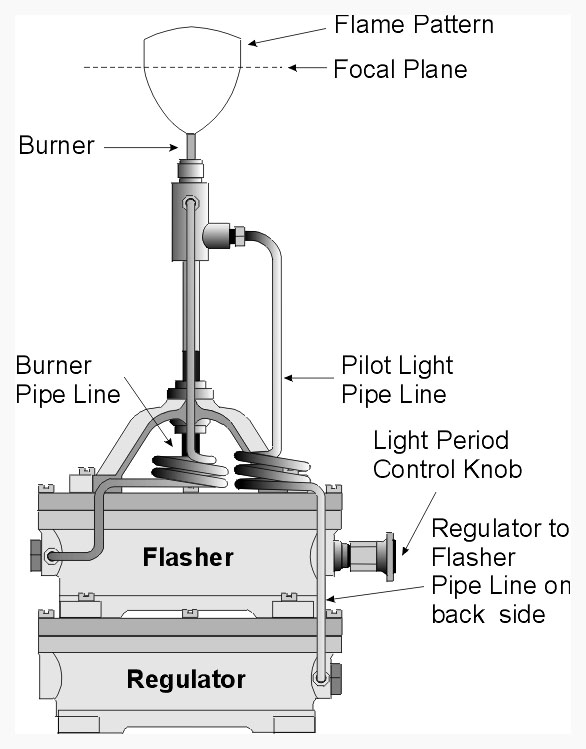
Flasher – An assembly within an Acetylene Lamp that causes the flame to rapidly change from almost no visible flame to a full sized flame. This action gives the illusion that the Acetylene Lamp is flashing.
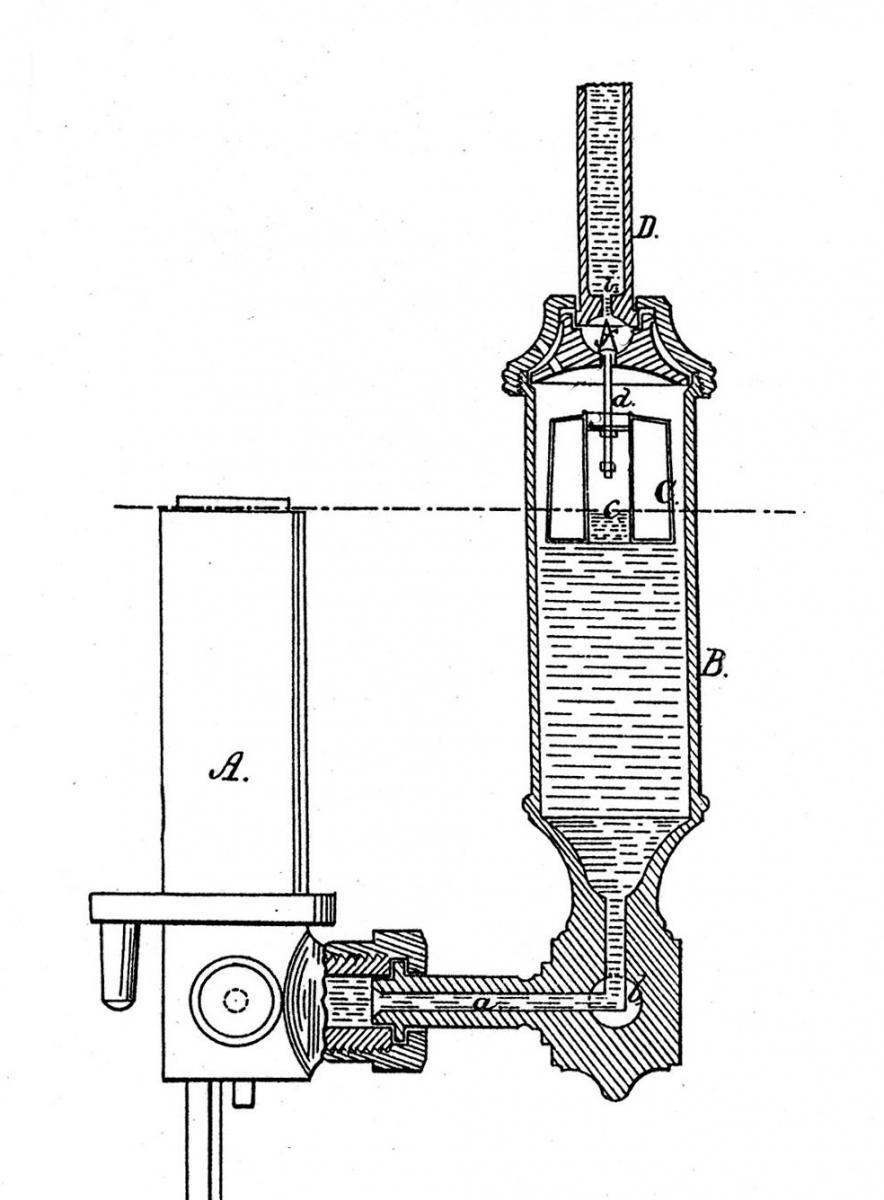
Float – An air filled metal tube that floats upon the fuel inside a glass tube. See item ‘C’ below.
Float Valve – A pin shaped metal rod attached to the top of the float. The pin rises and closes an opening from the upper fuel pipe shutting off fuel flow until some fuel is burned and the float lowers. See item ‘d’ below.
Fountain Lamp – A type of Constant Level Lamp. See Constant Level Lamp.
Frost Lamp – A small external lamp that was used to pre-heat the fuel in the main lamp’s reservoir.
Fuel Overflow Detector – The overflow of the oil passed over the concentric wicks and back down into the Drip Cup overflow collector and out a small tube into a Sensor Cup, which was a part of the Fuel Overflow Detector. An alarm bell was used with the lamps in Fresnel lens lights. It consisted of a lever that was pivoted like a teeter-totter. One end of the lever was raised and blocked the alarm mechanism. The other end of the lever held a small Sensor Cup with a small hole in its bottom. The Sensor Cup was located in the flow of the oil from the overflow of the burner. As long as oil overflowed the burner, the Sensor Cup was kept full of oil and the alarm lever was held in place. If the overflow of oil stopped, the Sensor Cup would cease to be filled and the oil within it would flow out through the small hole in its bottom. When this happened the alarm lever was no longer held in the up position and the end blocking the alarm mechanism lowered and the alarm would sound. The alarm usually consisted of a bell located in the tower or keeper’s quarters. After passing through the Sensor Cup the overflow oil was passed into the top of the Lower Reservoir through a small wire mesh strainer.
Fuel Pre-Heater – See Frost Lamp.
Fuel Pump – See Clockwork Pump.
Fuel Vaporizer – A Spirit Lamp or an auxiliary burner that is used to pre-heat a portion of the fuel pipe leading to the air intake of an Incandescent Oil Vapor burner. This pre-heating action vaporizes the fuel and allows it to spray onto the mantle providing the action necessary to make the mantle incandescent.
Funck – The foreman of the 3rd District Lamp Shop on Staten Island. Joseph Funck invented or improved most of the lamps used by the US Lighthouse Service.
Gallery – The metal platform surrounding the burner on which the chimney usually sits.
Gravity Feed – See Hydraulic Lamp.
Heap - The engineer of the 3rd District Depot on Staten Island. David Heap assisted Joseph Funck in improving a number of the lamps used by the US Lighthouse Service.
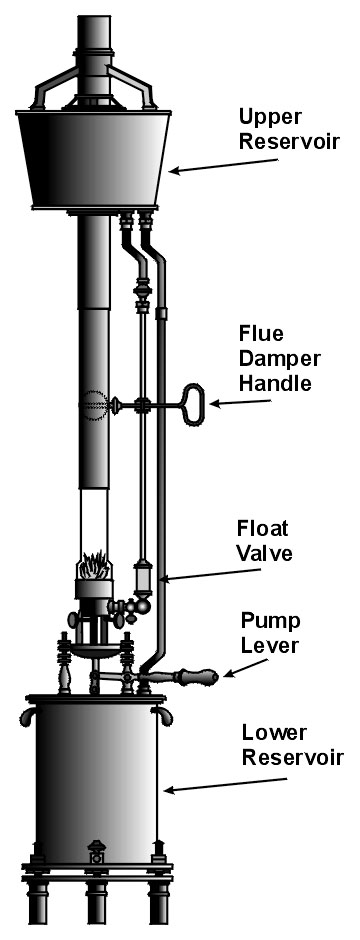
Hydraulic Lamp – A lamp where the fuel is held above the burner and is fed to the burner under the pressure of gravity where it overflows the wick(s). The fuel is initially placed in the lower reservoir and is then hand pumped to the upper reservoir.
Hydrostatic Lamp – A lamp that used the weight of a liquid slightly heavier than the oil, which would flow below the oil and force it up a tube to the wicks. The main drawback to the hydrostatic lamp was that it functioned based on the relatively minor difference in the density (specific gravity) of the zinc sulfate vs. that of the oil. If the density of the zinc sulfate solution was not exactly correct the oil would not flow at all or would flow much too quickly.
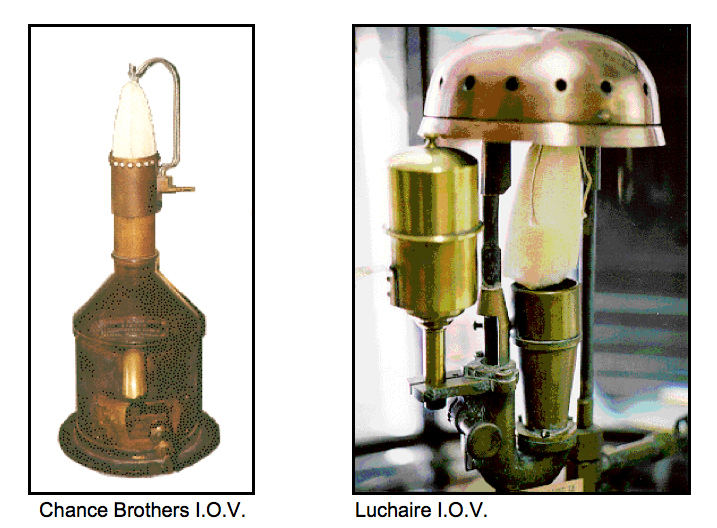
I.O.V. – The Incandescent Oil Vapor Lamp used air pressure and a fuel vaporizer tube where the kerosene was preheated into a fine gas vapor before it was ignited as a flame. This dramatically increased the oxygen at the flame and provided a brighter flame using less fuel.
Later an improved burner was designed in which the gas vapor flame ignited a mantle made of silk impregnated with zirconia. The I.O.V. Lamp produced at least three times the light output of the Argand style lamps previously used.
Two main styles of I.O.V. Lamps were used in America. They were the Chance Brothers I.O.V. Lamp and the Luchaire I.O.V. Lamp.
Light Period Control Knob – An adjusting knob on the side of an Acetylene Flasher that can be rotated to adjust the amount of time that the flame is on or off.
Lower Reservoir – The fuel storage container below the burner in a Hydraulic or Moderator Lamp.
Mantle – A small bag made of silk or cotton impregnated with chemicals that is used in Incandescent Oil Vapor Lamps.
Mantle Holder – A metal ring with a small vertical wire that holds the mantle. The Mantle Holder can be removed during the lamp lighting process.
Meth Tray – A Chance Brothers special very flat Spirit Lamp. See Spirit Lamp.
Moderator Lamp – A lamp where the fuel is fed to overflow the burner by the action of a large weighted piston inside the lower reservoir.

Needle Valve – Controlled the fuel flow to the burner. See Moderator Lamp drawing.
Oil Shut Off Valve – Used to turn the lamp off. See Moderator Lamp drawing.
Piston – The large weight that pressed on the fuel forcing it up to overflow the wicks in the burner. See Moderator Lamp drawing.
Piston Chain – The crank raised the chain that raised the piston. See Moderator Lamp drawing.
Piston Raising Crank – See Moderator Lamp drawing.
Pneumatic Lamp – A lamp using pressurized air to force the fuel to or over the wick(s).
Regulator – An assembly within an Acetylene Lamp that reduces the gas pressure from the acetylene storage cylinder and maintains a constant (much lower) pressure that is fed to the Flasher portion of the Acetylene Lamp.
Simplex Burner – A flat wick burner with one wick.
Spirit Lamp – A small auxiliary lamp with a one or two rope wicks used to pre-heat the fuel and cause it to vaporize in an Incandescent Oil Vapor Lamp.
Upper Reservoir – See Hydraulic Lamp drawing.
Wick Concentric – A series of wicks of graded sizes placed one within the other. Each wick size is placed in its own wick tube.
Wick Flat – A single wick shaped like a flat piece of ribbon.
Wick Riser – A shaft in contact with a wick that has small spines sticking into the wick. As the Wick Riser is turned the spines raise or lower the wick.
Wick Riser Knob – A small knob attached to the end of the Wick Riser shaft allowing it to be manually turned.
Wick Rope – A wick made with a solid center, like a piece of rope or clothesline.
Wick Tube – The metal tube formed by placing one thin walled metal pipe inside another. The space between the two pipes is the area where the wick is placed and the result is a wick tube holding the wick.